Well, with my last post, I was not able to join Hyper-v 3 to SCVMM 2012 RC. Therefore, most of labs can’t be done. After I cried loud, our MS TAM help me to find a new copy of SCVMM 2012 CTP. This version is designed for Windows 8 and all functions are in Go status!!
With this exciting news, I managed myself (thanks a lot to my team mates!) to get 3 HP G5 servers to build a test environment today. Just like all test labs, I spent lots of time to work hard to find solutions and I hope my post will save your time and let’s uncover Hyper-v 3 true power together!!
Again, if I made any mistakes, please feel free to point out.
Introduce my Test Lab:
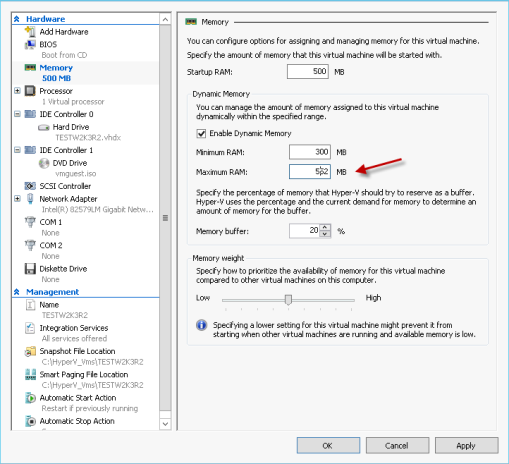
My test lab involves 3 physical hosts in the same subnet. There is no FC SANs available nor NAS exists. Each Hosts has it’s own local disks. I installed Windows 8 Beta on all 3 servers since this is one of conditions to do labs. 2 Servers I have enabled with Hyper-v 3 and I installed SCVMM 2012 CTP on the last server.
Note:
There is no issue of installing Windows 8. But with SCVMM, you need to install AIX and .NetFramework 3.5. You can’t tick the .NetFramework inside of W8, that would fail with not able to download. What you can do is following:
And restart server afterwards
Hyper-v 3 Storage vMotion is quite good
The one thing Hyper-v R2 can’t do is storage vMotion. Without this feature, I’m not able to migrate a live VM from one share LUN to another shared LUN without powering off VM. In the Hyper-v 3, MS not only managed to do a share storage vMotion in a cluster with SAN, you can storage vMotion between two standalone Hosts with a windows 8 share folder (SMB 2.2) !! (No more expensive VSA?).
Create a share folder
Live Migration is just normal vMotion with disk files sitting on the share storage. In this case, it’s a windows 8 share folder.
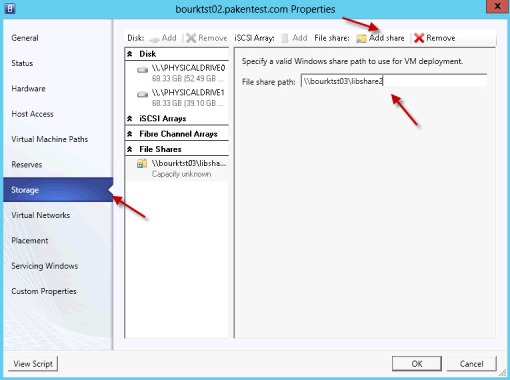
Since I have only local disks, I want to have some shared storages as the part of habit I got from Vmware. With Hyper-v 3, all what you need is a Windows 8 server and create a traditional share.
That’s it. No drama. No need for any specific share rights. This share purpose is to enable you to see this share when you add it into VMM. Once it is added, VMM will modify the accessing rights.
There are 2 steps to add this Share resource. The first steps is to add it to VMM library. so all VMs will sitting on that. You also need to add share resource to individual hosts so VMM will add hosts ID to security list.
Add to VMM Library
Add to individual host
Once it is added, your host is able to migrate VMs to share library.
This is how VMM setup access rights on the folder.
Storage vMotion (between host and share folder)
Basically, you can migrate VM files from local disk of your host to a share folder and from share folder to share folder or move it back to local disk.
According to my calculation, there is no ping drop during moving. The ping value sometimes is increase from 2ms to 65ms.
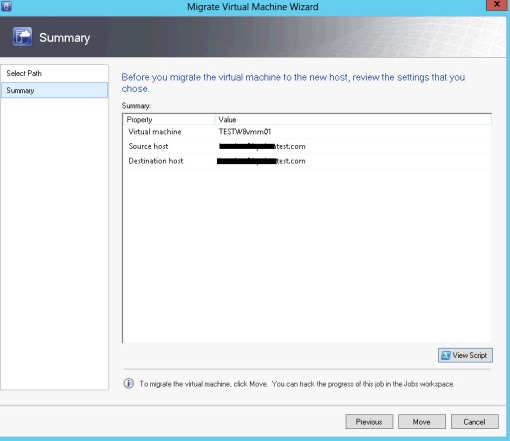
Storage vMotion from host to host
It’s interesting that MS say Hyper-v 3 is able to storage vMotion between two standalone host but they recommend to do it with a share folder accessable by both hosts. So does that mean you can Storage vMotion + vMotion from Stand alone host to stand alone host?
From my test result, It actually tried but failed at 81%. What it happened was Storage vMotion kicked in and copied 9GB data from one host to another host. During the copy procedure, the ping value jump up to 600ms. But the file is copied completely. Then, ping drop back to 2ms and tried to translate the last bit in the memory and that’s where it failed.
Overall, Hyper-v 3 can do Storage vMotion and with at least 2 sessions at same time. The ping value jump up can be contributed with my 100Mbit/s network limitation. Hyper-v 3 can use a normal windows 8 share folder as storage space which saves tons of money. so no more NAS and VSA? The new Windows 8 vhdx supports 64TB so there is no worries on how big a single file can be.
Bugs I have found:
1.With Windows 8 beta, RDP connection seems dropped if I started to copy large files via network. The whole server actually seems to be frozen status until copy is finished. My guess is that W8 didn’t prioritize RDP over copy session.
2.When I storage vMotion a VM which use differencing disk, the original disk (or parent disk) are not moved with storage vMotion.














 Note
Note