First of all, Happy New Year of 2013!! I am happy the whole world didn’t blow up and my guess those Mayan dudes just running out of space on that piece of stone so they think, why the hell I need to care about world in thousands years later? ![]()
Now, back to Vmware. With vSphere 5.1.0b released, I start to wonder whether it’s time to consider to use vDS (Virtual distribution switch) to replace VSS.
vDS has been around for years, only Enterprise plus license would actually use it. The concept of vDS is great, but the real world is not practical from my point of View to use vDS to complete replace VSS.
My suggestion is to have hybrid environment with vSS and vDS. As matter of fact, that , I’m afraid, is your only option. There will be time for you to failover VMs from broken vDS to something else, so between another vDS and vSS, which one you would go?
I did a little bit research regarding vDS and I would like to share some tricks and “how to” to everyone. Feel free to pop up question and correct my mistakes as usual.
vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client?
Now, with vSphere Web Client getting more and more popular, should we use Web Client and dump old one? The answer is No. The new Web Client is incompleted, slow but it does provide more functions than C++ version. I will stick with Web client in this post as much as possible.
What’s is vDS?
You can always find this answer from my old post here. Comparing with vSS, vDS provide more virtual gateways (not like vSS, vDS also virtualize Uplink). More control and monitoring on the traffic going through virtual switch and also profile base deploying from vCenter to Hosts so vDS is aware all hosts network rather than working alone like vSS.
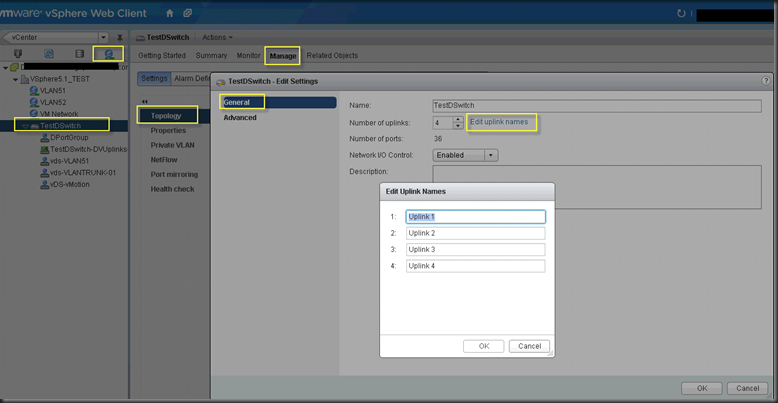
However, it does bring lots of other issue if you want to put vDS into production. One of few issues is to rename Uplink.
Why do we need to rename Uplink?
Uplink exists on vDS only. It’s a virtual port group which you connects your physical nics to. Assuming you have 10 hosts, it’s hard to guarantee all vmnic01 will connect to Uplink01 since vmnic01 may connect to different network in the real world. After a while, you may get confused about what each Uplink for.
Tricks:
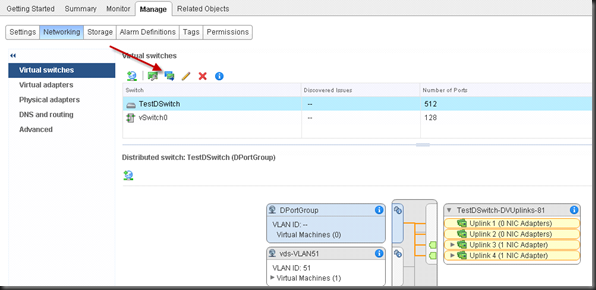
Always rename your Uplink before you start to connect anything to vDS.
You need to rename your Uplink ASAP after you create your vDS. Once vDS is hook up something, it simply won’t let you touch Uplink because it may connect to something. Even if you remove the connection to another link, the vDS will still hold same configuration till refresh time. (for me details and solution, please check my old post).
Steps to rename Uplink
Login to Web Client,
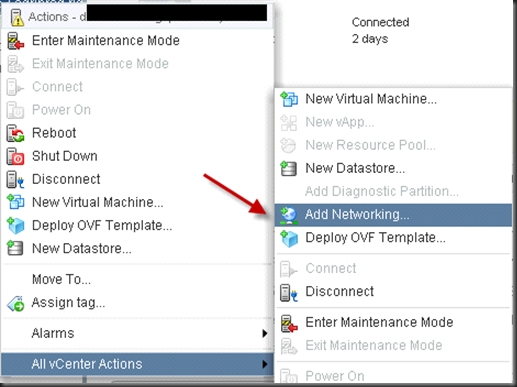
After you rename your Uplink, you can start to create vMotion group for vDS.
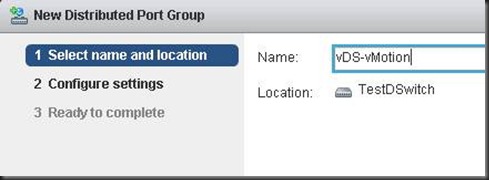
Create vMotion for vDS
The funny thing for this step is you have to create a vDS port group first before you can do anything lese.
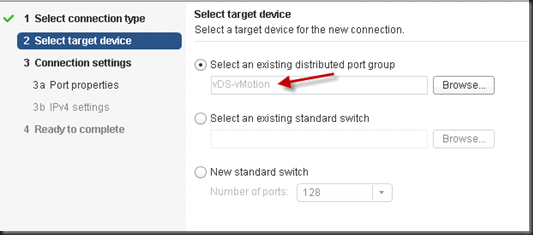
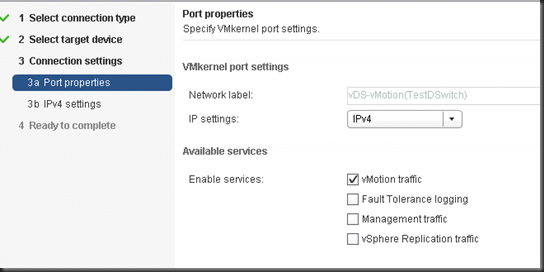
Now, you can create a new Uplink for vMotion
I skip the rest of parts.
Tricks:
I don’t think you can vMotion between vss and vDS. You can only vmotion between same type of vSwitch. Although you can migrate vms from VSS to vDS with few ping drops.
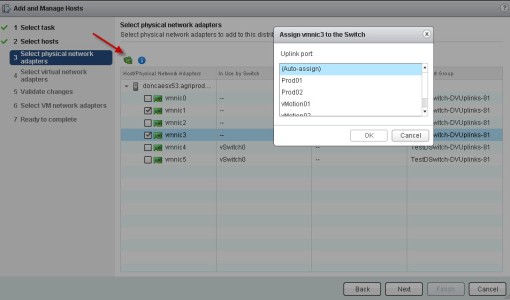
Assign specific vmnic to Uplink
One thing you would like to do is to assign vmnic01 (for example) to a specific Uplink. Please follow these steps.
Add Physical adapters into vDS via web client
change Auto-assign to a specific Uplink
Delete a Uplink (not physical nic connection)
The simple thing I want to do is to remove one of Uplinks. It’s virtual Uplink on vSwitch, it is NOT the physical nic which I connect to Uplink. but this very simple thing almost can’t be done via either vSphere Client or Web client.
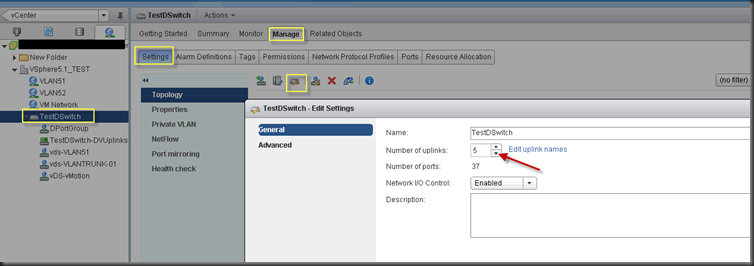
To give you a better understanding, a new vDS coming with 4 Uplinks connecting with nothing. What happen if I add more uplinks now and want to remove some Uplinks latter?
The way you add more Uplink is here
Unfortunately, the only way to remove Uplink is either rebuild a new vDS or migrate all your VMs to other switch and remove all physical host nic connection to Uplink and go back to here and to set a LOWER number!
If you set this number to 3, 2 uplinks will disappear but it won’t let you choose which 2 uplinks. Therefore, you better move all VMs and connections between physical host nics to Uplink before you remove Uplink.
This is not just my conclusion, a Vmware Support Engineer was on the phone 1 hour with me and come up with this solution. Maybe there is another way to do it, but we are not able to find out. If you know how to do it, please let me know or leave it in comment.
Conclusion:
There are still lots testing we can do with vDS, but at this stage, I definitely wouldn’t recommend to ditch vSS and use vDS solely. A hybrid environment is what I would recommend.
![clip_image002[5] clip_image002[5]](https://geeksilver.files.wordpress.com/2013/01/clip_image0025_thumb.jpg?w=493&h=310)
![clip_image002[7] clip_image002[7]](https://geeksilver.files.wordpress.com/2013/01/clip_image0027_thumb.jpg?w=502&h=238)

![clip_image002[6] clip_image002[6]](https://geeksilver.files.wordpress.com/2012/12/clip_image0026_thumb.jpg?w=463&h=348)
![clip_image002[8] clip_image002[8]](https://geeksilver.files.wordpress.com/2012/12/clip_image0028_thumb.jpg?w=473&h=356)
![clip_image002[10] clip_image002[10]](https://geeksilver.files.wordpress.com/2012/12/clip_image00210_thumb.jpg?w=475&h=359)
![clip_image002[14] clip_image002[14]](https://geeksilver.files.wordpress.com/2012/12/clip_image00214_thumb.jpg?w=441&h=334)
![clip_image002[16] clip_image002[16]](https://geeksilver.files.wordpress.com/2012/12/clip_image00216_thumb.jpg?w=465&h=350)